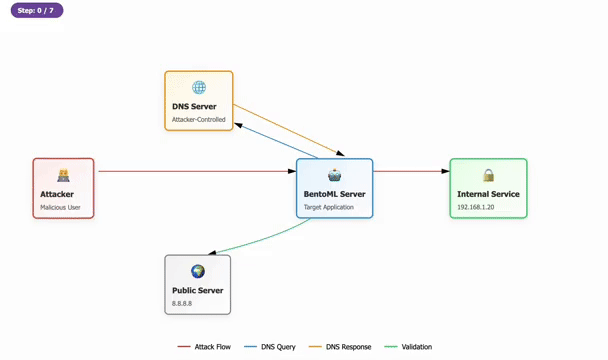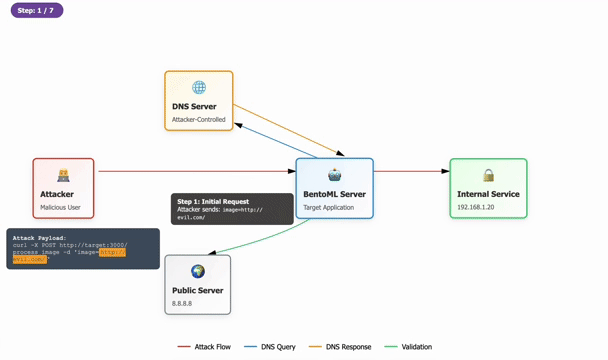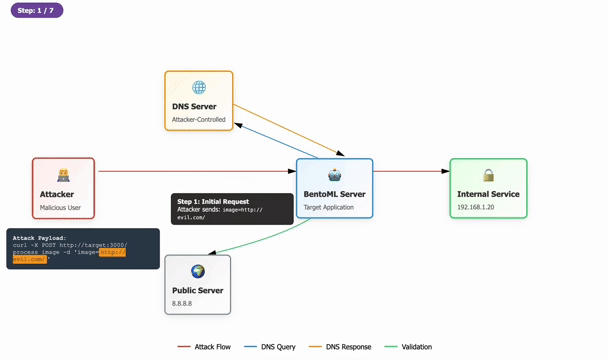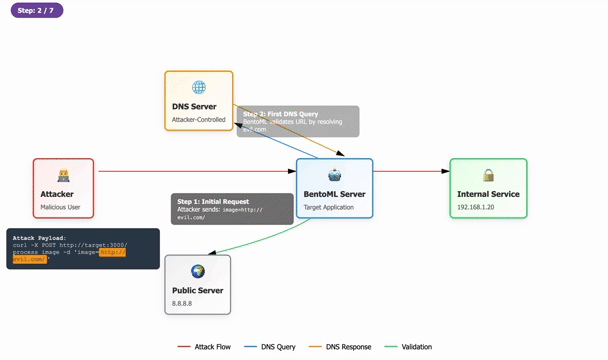
Tenable Research recently identified a significant issue concerning a bypass of the initial patch intended to fix a critical server-side request forgery (SSRF) vulnerability tracked as CVE-2025-54381 in BentoML. This popular open source tool is widely utilized for deploying AI applications. The original vulnerability permitted remote, unauthenticated attackers to invoke arbitrary HTTP requests, posing a major risk to sensitive internal resources. After realizing the flaw, Tenable has now provided a complete patch that users are urged to apply immediately to mitigate potential security risks.
Originally, the vulnerability received a CVSS score of 9.9, reflecting its potential severity. However, depending on network configurations, the practical risk it posed could vary, falling between scores of 5.3 to 8.6. The implementation of the patch included an ‘is_safe_url’ function for validating incoming URLs, aiming to block requests to unsafe domains. Unfortunately, the patching process has notable weaknesses: it allows alternative internal DNS addresses and certain public IPs tied to cloud providers, which can easily be exploited through a DNS rebinding attack, highlighting a crucial oversight in the patch’s defensive measures.
Tenable’s findings underscore the need for developers to rigorously address security vulnerabilities, particularly as their applications become more integrated with sensitive operations. Organizations using BentoML are recommended to upgrade to version 1.4.22 or later without delay to ensure compliance with the latest security standards. Failure to implement these updates could leave systems exposed to exploitation, making timely action paramount for maintaining overall cybersecurity hygiene.
👉 Pročitaj original: Tenable Research